IELTS Online
Giải đề thi Endless Harvest IELTS Reading [FULL ANSWER]
Mục lục [Ẩn]
Nhiều thí sinh gặp khó khăn khi luyện đề Endless Harvest – IELTS Reading Answers: từ việc chưa nắm vững từ vựng chuyên ngành, khó tìm thông tin chi tiết, đến mất quá nhiều thời gian phân tích câu hỏi. Bài viết này sẽ cung cấp đáp án chi tiết, phân tích từng câu và từ vựng quan trọng, giúp bạn nắm chắc nội dung bài đọc và nâng band điểm Reading hiệu quả.
1. Đề thi Endless Harvest IELTS Reading
Reading Passage
Endless Harvest
More than two hundred years ago, Russian explorers and fur hunters landed on the Aleutian Islands, a volcanic archipelago in the North Pacific, and learned of a land mass that lay farther to the north. 'The islands’ native inhabitants called this land mass Aleyska, the ‘Great Land’; today, we know it as Alaska.
The forty-ninth state to join the United States of America (in 1959), Alaska is fully one-fifth the size of the mainland 48 states combined. It shares, with Canada, the second longest river system in North America and has over half the coastline of the United States. The rivers feed into the Bering Sea and Gulf of Alaska - cold, nutrient-rich waters which support tens of millions of seabirds, and over 400 species of fish, shellfish, crustaceans, and molluscs. Taking advantage of this rich bounty, Alaska’s commercial fisheries have developed into some of the largest in the world.
According to the Alaska Department of Fish and Game (ADF&G), Alaska’s commercial fisheries landed hundreds of thousands of tonnes of shellfish and herring, and well over a million tonnes of groundfish (cod, sole, perch and pollock) in 2000. The true cultural heart and soul of Alaska’s fisheries, however, is salmon. ‘Salmon,’ notes writer Susan Ewing in The Great Alaska Nature Factbook, ‘pump through Alaska like blood through a heart, bringing rhythmic, circulating nourishment to land, animals and people.’ The ‘predictable abundance of salmon allowed some native cultures to flourish,’ and ‘dying spawners* feed bears, eagles, other animals, and ultimately the soil itself.’ All five species of Pacific salmon - chinook, or king; chum, or dog; coho, or silver; sockeye, or red; and pink, or humpback - spawn** in Alaskan waters, and 90% of all Pacific salmon commercially caught in North America are produced there. Indeed, if Alaska was an independent nation, it would be the largest producer of wild salmon in the world. During 2000, commercial catches of Pacific salmon in Alaska exceeded 320,000 tonnes, with an ex-vessel value of over $US 260 million.
Catches have not always been so healthy. Between 1940 and 1959, overfishing led to crashes in salmon populations so severe that in 1953 Alaska was declared a federal disaster area. With the onset of statehood, however, the State of Alaska took over management of its own fisheries, guided by a state constitution which mandates that Alaska’s natural resources be managed on a sustainable basis. At that time, statewide harvests totalled around 25 million salmon. Over the next few decades average catches steadily increased as a result of this policy of sustainable management, until, during the 1990s, annual harvests were well in excess of 100 million, and on several occasions over 200 million fish.
The primary reason for such increases is what is known as ‘In-Season Abundance-Based Management’. There are biologists throughout the state constantly monitoring adult fish as they show up to spawn. The biologists sit in streamside counting towers, study sonar, watch from aeroplanes, and talk to fishermen. The salmon season in Alaska is not pre-set. The fishermen know the approximate time of year when they will be allowed to fish, but on any given day, one or more field biologists in a particular area can put a halt to fishing. Even sport fishing can be brought to a halt. It is this management mechanism that has allowed Alaska salmon stocks - and, accordingly, Alaska salmon fisheries — to prosper, even as salmon populations in the rest of the United States are increasingly considered threatened or even endangered.
In 1999, the Marine Stewardship Council (MSC)*** commissioned a review of the Alaska salmon fishery. The Council, which was founded in 1996, certifies fisheries that meet high environmental standards, enabling them to use a label that recognises their environmental responsibility. The MSC has established a set of criteria by which commercial fisheries can be judged. Recognising the potential benefits of being identified as environmentally responsible, fisheries approach the Council requesting to undergo the certification process. The MSC then appoints a certification committee, composed of a panel of fisheries experts, which gathers information and opinions from fishermen, biologists, government officials, industry representatives, non-governmental organisations and others.
Some observers thought the Alaska salmon fisheries would not have any chance of certification when, in the months leading up to MSC’s final decision, salmon runs throughout western Alaska completely collapsed. In the Yukon and Kuskokwim rivers, chinook and chum runs were probably the poorest since statehood; subsistence communities throughout the region, who normally have priority over commercial fishing, were devastated.
The crisis was completely unexpected, but researchers believe it had nothing to do with impacts of fisheries. Rather, they contend, it was almost certainly the result of climatic shifts, prompted in part by cumulative effects of the el niño/la niña phenomenon on Pacific Ocean temperatures, culminating in a harsh winter in which huge numbers of salmon eggs were frozen. It could have meant the end as far as the certification process was concerned. However, the state reacted quickly, closing down all fisheries, even those necessary for subsistence purposes.
In September 2000, MSC announced that the Alaska salmon fisheries qualified for certification. Seven companies producing Alaska salmon were immediately granted permission to display the MSC logo on their products. Certification is for an initial period of five years, with an annual review to ensure that the fishery is continuing to meet the required standards.
Questions 14-20
Do the following statements agree with the information given in Reading Passage 159?
In boxes 14-20 on your answer sheet, write
TRUE if the statement agrees with the information
FALSE if the statement contradicts the information
NOT GIVEN if there is no information on this
- 14. The inhabitants of the Aleutian islands renamed their islands Aleyska
- 15. Alaska's fisheries are owned by some of the world's largest companies.
- 16. Life in Alaska is dependent on salmon.
- 17. Ninety per cent of all Pacific salmon caught are sockeye or pink salmon.
- 18. More than 320,000 tonnes of salmon were caught in Alaska in 2000.
- 19. Between 1940 and 1959, there was a sharp decrease in Alaska's salmon population.
- 20. During the 1990s, the average number of salmon caught each year was 100 million.
Questions 21-26
Complete each sentence with the correct ending, A-K. below.
Write the correct letter, A-K. in boxes 21-26 on your answer sheet.
21 In Alaska, biologists keep a check on adult fish
22 Biologists have the authority
23 In-Season Abundance-Based Management has allowed the Alaska salmon fisheries
24 The Marine Stewardship Council (MSC) was established
25 As a result of the collapse of the salmon runs in 1999, the state decided
26 In September 2000, the MSC allowed seven Alaska salmon companies
- A to recognise fisheries that care for the environment.
- B to be successful.
- C to stop fish from spawning
- D to set up environmental protection laws.
- E to stop people fishing for sport.
- F to label their products using the MSC logo.
- G to ensure that fish numbers are sufficient to permit fishing.
- H to assist the subsistence communities in the region.
- I to freeze a huge number of salmon eggs.
- J to deny certification to the Alaska fisheries.
- K to close down all-fisheries.
>> Xem thêm: Giải đề Does Education fuel economic growth IELTS Reading
2. Đáp án đề thi Endless Harvest IELTS Reading
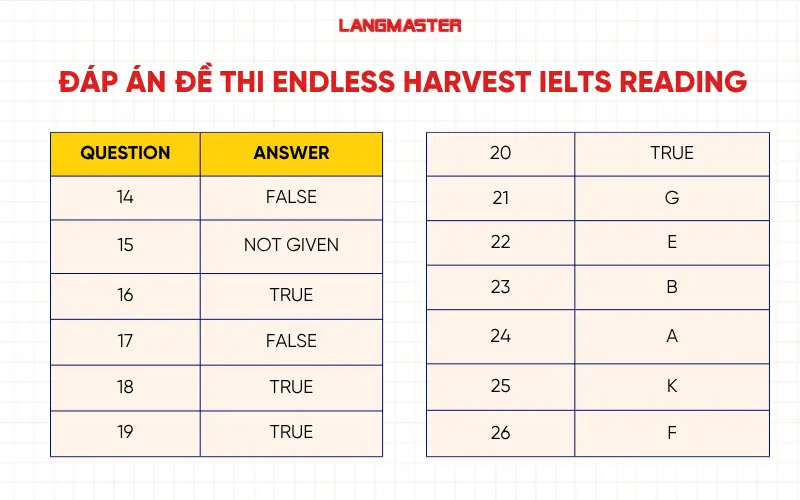
14. Đáp án: FALSE
Thông tin trong bài: “The islands’ native inhabitants called this land mass Aleyska, the ‘Great Land’; today, we know it as Alaska.”
Giải thích: Người bản địa gọi vùng đất là Aleyska, nhưng họ không phải là người đổi tên các đảo.
15. Đáp án: NOT GIVEN
Thông tin trong bài: Bài nói về “Alaska’s commercial fisheries have developed into some of the largest in the world,” nhưng không đề cập ai sở hữu.
16. Đáp án: TRUE
Thông tin trong bài: “Salmon… bring rhythmic, circulating nourishment to land, animals and people.”
Giải thích: Cá hồi cung cấp thức ăn thiết yếu cho động vật, con người và cả đất, nên đời sống ở Alaska phụ thuộc nhiều vào cá hồi.
17. Đáp án: FALSE
Thông tin trong bài: “All five species of Pacific salmon … spawn in Alaskan waters, and 90% of all Pacific salmon commercially caught in North America are produced there.”
Giải thích: 90% đề cập đến tất cả cá hồi Thái Bình Dương được sản xuất ở Alaska, không chỉ riêng sockeye hay pink.
18. Đáp án: TRUE
Thông tin trong bài: “During 2000, commercial catches of Pacific salmon in Alaska exceeded 320,000 tonnes.”
Giải thích: Thông tin này hoàn toàn trùng khớp với bài.
19. Đáp án: TRUE
Thông tin trong bài: “Between 1940 and 1959, overfishing led to crashes in salmon populations…”
Giải thích: “Crashes” nghĩa là giảm mạnh về số lượng cá hồi.
20. Đáp án: TRUE
Thông tin trong bài: “…during the 1990s, annual harvests were well in excess of 100 million…”
Giải thích: Thông tin trong bài xác nhận số lượng cá đánh bắt trung bình hàng năm vượt 100 triệu con.
21. Đáp án: G
Thông tin trong bài: “There are biologists throughout the state constantly monitoring adult fish as they show up to spawn… The salmon season in Alaska is not pre-set… one or more field biologists in a particular area can put a halt to fishing.”
Giải thích: Họ theo dõi số lượng cá để đảm bảo có đủ cá cho phép đánh bắt.
22. Đáp án: E
Thông tin trong bài: “Even sport fishing can be brought to a halt.”
Giải thích: Các nhà sinh vật học có quyền ngừng cả việc câu cá giải trí nếu cần.
23. Đáp án: B
Thông tin trong bài: “It is this management mechanism that has allowed Alaska salmon stocks – and, accordingly, Alaska salmon fisheries — to prosper…”
Giải thích: Quản lý theo mùa giúp ngư trường Alaska phát triển và thành công.
24. Đáp án: A
Thông tin trong bài: “The Council, which was founded in 1996, certifies fisheries that meet high environmental standards, enabling them to use a label that recognises their environmental responsibility.”
Giải thích: MSC được thành lập để công nhận các ngư trường có trách nhiệm với môi trường.
25. Đáp án: K
Thông tin trong bài: “However, the state reacted quickly, closing down all fisheries, even those necessary for subsistence purposes.”
Giải thích: Do sự sụp đổ của đàn cá hồi, bang đã quyết định đóng tất cả các ngư trường.
26. Đáp án: F
Thông tin trong bài: “Seven companies producing Alaska salmon were immediately granted permission to display the MSC logo on their products.”
Giải thích: MSC cho phép 7 công ty sử dụng logo MSC trên sản phẩm của họ.
>> Xem thêm:
- Giải đề IELTS Reading: Venus Flytrap (FULL ANSWERS)
- Roman shipbuilding and navigation [IELTS Reading Cambridge 16 – Test 3]
3. Từ vựng quan trọng đề Endless Harvest IELTS Reading
Để nắm chắc bài đọc “Endless Harvest”, việc hiểu và ghi nhớ các từ vựng chuyên môn là cực kỳ quan trọng. Dưới đây là những từ vựng trong đề thi IELTS Reading Endless Harvest:
Archipelago
- Nghĩa: Quần đảo, nhóm đảo
- Ví dụ trong bài: “Russian explorers and fur hunters landed on the Aleutian Islands, a volcanic archipelago…”
Nutrent-rich
- Nghĩa: Giàu chất dinh dưỡng
- Ví dụ trong bài: “Bering Sea and Gulf of Alaska – cold, nutrient-rich waters…”
Species
- Nghĩa: Loài (động vật, thực vật)
- Ví dụ trong bài: “Over 400 species of fish, shellfish, crustaceans, and molluscs.”
Pawn/ Spawning
- Nghĩa: Sinh sản (cá, tôm, ếch…); đẻ trứng
- Ví dụ trong bài: “All five species of Pacific salmon spawn in Alaskan waters.”
Overfishing
- Nghĩa: Đánh bắt quá mức
- Ví dụ trong bài: “Between 1940 and 1959, overfishing led to crashes in salmon populations.”
Sustainable management/ sustainable basis
- Nghĩa: Quản lý bền vững / trên cơ sở bền vững
- Ví dụ trong bài: “…Alaska’s natural resources be managed on a sustainable basis.”
Crisis
- Nghĩa: Khủng hoảng, tình trạng nghiêm trọng
- Ví dụ trong bài: “The crisis was completely unexpected…”
Certification/ Certify
- Nghĩa: Chứng nhận / cấp giấy chứng nhận
- Ví dụ trong bài: “The Alaska salmon fisheries qualified for certification.”
Abundance
- Nghĩa: Sự dồi dào, phong phú
- Ví dụ trong bài: “In-Season Abundance-Based Management…”
Subsistence communities
- Nghĩa: Cộng đồng sinh sống dựa vào nguồn tài nguyên tự nhiên
- Ví dụ trong bài: “Subsistence communities throughout the region were devastated.”
Biologist
- Nghĩa: Nhà sinh vật học
- Ví dụ trong bài: “There are biologists throughout the state constantly monitoring adult fish…”
Collapse
- Nghĩa: Sụp đổ, suy giảm nghiêm trọng
- Ví dụ trong bài: “Salmon runs throughout western Alaska completely collapsed.”
4. Khóa IELTS online tại Langmaster
Nhiều thí sinh khi luyện đề Endless Harvest – IELTS Reading Answers thường gặp phải các khó khăn như: không nắm vững từ vựng chuyên ngành, chưa thành thạo kỹ năng tìm thông tin chi tiết trong bài, hay mất quá nhiều thời gian để phân tích câu hỏi. Điều này khiến việc luyện Reading trở nên căng thẳng, đặc biệt với những bạn mới bắt đầu hoặc lâu không luyện tập tiếng Anh.
Nếu bạn muốn cải thiện hiệu quả kỹ năng IELTS Reading và chinh phục các bài đọc khó như Endless Harvest, Langmaster chính là lựa chọn lý tưởng. Với hơn 16 năm kinh nghiệm Langmaster – trung tâm luyện thi IELTS uy tín và chất lượng hàng đầu Việt Nam đã đồng hành cùng hàng nghìn học viên nâng band điểm chỉ sau vài tháng học bài bản theo lộ trình cá nhân hóa.
Điểm mạnh của khóa IELTS online tại Langmaster là mô hình lớp nhỏ (7–10 học viên), giúp giáo viên theo sát từng học viên. Trong mỗi buổi học, bạn sẽ được sửa lỗi chi tiết, luyện tập kỹ năng đọc hiểu chuyên sâu và phản xạ nhanh với các dạng bài IELTS Reading, bao gồm cả những chủ đề phức tạp như Endless Harvest và các kỹ năng khác của kỳ thi IELTS.
Đội ngũ giáo viên tại Langmaster đều có chứng chỉ IELTS 7.5+, được đào tạo bài bản về phương pháp giảng dạy và luôn tận tâm đồng hành cùng học viên. Các bài tập của bạn sẽ được chấm chữa chi tiết trong 24h, giúp bạn nắm rõ điểm mạnh, điểm yếu từ đó cải thiện nhanh chóng
Trước khi bắt đầu khóa học, học viên sẽ được kiểm tra trình độ 4 kỹ năng để xác định band hiện tại, từ đó xây dựng lộ trình học tập cá nhân hóa theo mục tiêu band điểm. Trong quá trình học, bạn còn nhận báo cáo tiến độ hàng tháng, coaching 1-1 với chuyên gia IELTS, cùng cam kết đầu ra bằng văn bản – học lại miễn phí nếu chưa đạt mục tiêu.
Langmaster hiện triển khai chương trình HỌC THỬ MIỄN PHÍ, giúp bạn trải nghiệm phương pháp giảng dạy hiện đại, môi trường học chuyên nghiệp và đội ngũ giáo viên tận tâm. Đăng ký ngay hôm nay để tiến gần hơn đến band điểm IELTS bạn mong muốn!
Nội Dung Hot
KHÓA TIẾNG ANH GIAO TIẾP 1 KÈM 1
- Học và trao đổi trực tiếp 1 thầy 1 trò.
- Giao tiếp liên tục, sửa lỗi kịp thời, bù đắp lỗ hổng ngay lập tức.
- Lộ trình học được thiết kế riêng cho từng học viên.
- Dựa trên mục tiêu, đặc thù từng ngành việc của học viên.
- Học mọi lúc mọi nơi, thời gian linh hoạt.

KHÓA HỌC IELTS ONLINE
- Sĩ số lớp nhỏ (7-10 học viên), đảm bảo học viên được quan tâm đồng đều, sát sao.
- Giáo viên 7.5+ IELTS, chấm chữa bài trong vòng 24h.
- Lộ trình cá nhân hóa, coaching 1-1 cùng chuyên gia.
- Thi thử chuẩn thi thật, phân tích điểm mạnh - yếu rõ ràng.
- Cam kết đầu ra, học lại miễn phí.

KHÓA TIẾNG ANH TRẺ EM
- Giáo trình Cambridge kết hợp với Sách giáo khoa của Bộ GD&ĐT hiện hành
- 100% giáo viên đạt chứng chỉ quốc tế IELTS 7.0+/TOEIC 900+
- X3 hiệu quả với các Phương pháp giảng dạy hiện đại
- Lộ trình học cá nhân hóa, con được quan tâm sát sao và phát triển toàn diện 4 kỹ năng
Bài viết khác

Các dạng bài phổ biến và tiêu chí chấm điểm IELTS Reading chi tiết nhất: Multiple Choice, Matching Information, Matching Headings,... và hướng dẫn chiến lược làm bài hiệu quả

Những sai lầm khi luyện IELTS Reading bao gồm: dịch từng từ, đọc hết cả bài, không đọc câu hỏi trước, không quản lý thời gian, không nắm vững kỹ năng paraphrase, viết sai chính tả
![Giải đề IELTS Reading: A brief history of humans and food [full answers]](https://langmaster.edu.vn/storage/images/2025/09/20/a-brief-history-of-humans-and-food-ielts-reading-answers.webp)
Giải đề thi IELTS Reading “A brief history of humans and food” kèm full đề thi thật, câu hỏi, đáp án, giải thích chi tiết, và từ vựng cần lưu ý khi làm bài.

Tổng hợp IELTS Reading tips hay nhất giúp bạn đọc nhanh, nắm ý chính và xử lý thông tin chính xác, tự tin đạt điểm cao trong kỳ thi IELTS.
![Giải đề IELTS Reading: The importance of law [Full answers]](https://langmaster.edu.vn/storage/images/2025/09/22/55.webp)
Giải đề IELTS Reading “The importance of law” kèm đáp án chi tiết, từ vựng quan trọng và bí quyết luyện thi hiệu quả để nâng cao band điểm.





![Giải đề IELTS Reading: How deserts are formed [Full answers]](https://langmaster.edu.vn/storage/uploads/original/2025/10/22/ielts-reading-how-deserts-are-formed.png)

![Roman shipbuilding and navigation [IELTS Reading Cambridge 16 – Test 3]](https://langmaster.edu.vn/storage/uploads/original/2025/10/23/roman-shipbuilding-and-navigation.png)